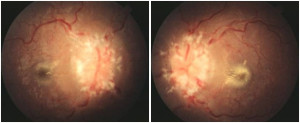
- Bilateral swelling of the optic nerve due to increased intracranial pressure
- Commonly associated with headaches, TVO’s, and pulsatile tinnitus
- Typically caused by an intracranial mass, malignant hypertension, or idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Management
- Visual field (enlarged blind spot), Optic nerve imaging (OCT)
- Emergent MRI of brain and orbit, lumbar puncture
- Check blood pressure